How To Eat A Healthy Plant-based Diet
Choosing to eat a plant-based diet is a personal choice. What are your reasons?
Some people choose to live a vegan lifestyle because they believe in not harming animals. Others see it as a positive step towards planetary health. Many eat a plant-based diet for personal health reasons.
Whatever your reasons, the next question is "How are you going to live it?" If you're here, we hope you want to optimize your own health as well as that of the planet. Increasing your knowledge base will help you make these important decisions. Whether you're transitioning to vegan or have eaten a plant-based diet for years, it’s important to examine what a plant-based diet offers you as well as what it doesn’t.
If an NFL quarterback can meet his high-demand nutritional needs on a plant-based diet, it certainly gives us confidence that we can too.
Not everyone thrives on a vegan diet. It’s easy to be an unhealthy or a junk-food vegan, especially with the plethora of processed plant-based foods available today.
A vegan diet has the potential to exceed all of your nutritional requirements or fall disappointingly short. A healthy vegan diet can provide you and the planet with optimal health. We define "healthy vegan diet" as a diet that meets or exceeds the average person's nutrient requirements according to the USDA and WHO. We're here to help you understand how easy it is to eat a healthy vegan diet.
With the knowledge to make smart choices, a plant based diet can exceed the nutrient levels you need to for optimal health.
If you’re a new vegan, you may be focused on the foods you're not eating rather than optimizing your nutrition through the foods you are eating. There is a beautiful and adventurous path ahead of you! A plant-based diet can be filled with delicious, satisfying, and nutritious meals. It's so much more than salads and veggie burgers! Being a smart vegan from the start ensures that you'll be eating the most healthy diet on the planet while optimizing your health for a long and vital life.
We bring families together around food.
Let's explore the most delicious and nutritious family diet for you and y our family. Schedule a complimentary call with us: Schedule my call now!
Why listen to us?
Markus ("Papa" of Your Vegan Family) has been vegan for 26 years. He graduated from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and attended Harvard University where he earned a Bachelor of Science in molecular biology with a concentration in creative writing. Stacy ("Mama" of Your Vegan Family) earned a Masters of Acupuncture degree after an undergraduate background in biology and health sciences. We've each amassed decades and a breadth of experience in science and health care: Markus served as a management consultant in New York and London for a firm specializing in the medical device, diagnostic, pharmaceutical and biotech industries, as well as co-managing a $320 million biotherapeutic for heart attack, pulmonary embolism and acute ischemic stroke while working with and learning from doctors and hospitals around the world. He also ran 100's of acute emergency medicine calls as a trained EMT/Firefighter for 6 years.
As a licensed Asian Medicine practitioner, Stacy served hundreds of clients for over 25 years in private practice as an acupuncturist and health/lifestyle consultant. Many of her client relationships spanned decades and generations of families. Each of us has shared our enthusiasm for the human body and the way it moves through teaching yoga in myriad settings to clients of all ages and skill levels. Together, we celebrate our passion for science, adventure travel, nature connection, family life, and plant-based, world fusion cuisine.
Being vegan is not a fad for us. It’s our way of family living that includes our two young boys ages 10 and 6 years who have been vegan since conception and thriving academically, physically, emotionally and spiritually ever since.
To help you understand and actualize a healthy vegan lifestyle, we do the research and share current health information and data while capitalizing on our decades of experience. We provide our favorite, world-fusion, plant-based recipes that include in-depth nutrient analysis for delicious, nutritious eating while providing security that you are eating healthy and safely for both you and your family.
For additional personal support, you can join Your Thriving Vegan Family Community. It's a private forum for vegan families and plant-based enthusiasts to ask questions, provide insight and inspiration, and receive personal responses from all of us at Your Vegan Family, including a kids thread! Click here to join us!
What is a Healthy Vegan Diet?
A vegan diet is a plant-based diet consisting of fruit, vegetables, grains, nuts, seeds, pulses (dried seeds of the legume family including lentils, beans, chickpeas, and dried peas), and their derivatives. Vegans do NOT eat animal-sourced foods including red meat, chicken, seafood, pork, butter, dairy, or honey.
A HEALTHY vegan diet meets or exceeds nutritional requirements that support personal health by eating across a broad range of unprocessed, nutrient-dense, plant-based foods with plant-sourced vitamin supplementation when necessary. A healthy vegan diet includes raw foods and smart hydration.
Keep in mind that a vegan diet may not be right for everyone. We all have different needs, digestive functions, and genetics. It is always your personal responsibility to monitor your health, listen to your body, and gather the data you need to make the right choices for you. The information we publish on Your Vegan Family is meant to be a resource for you, not nutritional advice.
Eating a healthy vegan diet supports not only personal health but also planetary health when you:
- choose organic and sustainably grown foods,
- source your food locally,
- minimize packaging,
- purchase from ecological and socially ethical companies.
Myths of a Plant-Based Diet
People unfamiliar with a plant-based diet sometimes have false ideas about it. These myths can scare people away from a vegan diet. Let's bust them right now and explore how you can ensure you're getting all the nutrients you need for a strong and body.
Common questions people ask about a plant-based diet are:
- Where do you get your Vitamin D, B12, Calcium, and Iron?
- How do you get enough protein?
- Aren't vegans weak and skinny?
- Don't vegans mostly eat salad?
We'll cover answers to those questions and more on this page.

Smart Vegan Nutrition
When we eat across a broad range of foods we are more likely to ingest the nutrients and calories we need for optimal health. Vegans who do this easily exceed most of their nutrient requirements.
When you remove animal-based products from your diet you may not know what to eat to replace some of the vitamins they're rich in. We'll help you get that sorted.
Food manufacturers, including plant-based food companies, know that people, no matter what their diet, tend to certain vitamin deficiencies and so they fortify foods like cereals, bread, and milk (dairy and plant-based milks) with Vitamin D, iron, calcium, and B vitamins. Fortified foods do not tend to use the highest quality and most bioavailable forms of nutrients. Sourcing your nutrition from whole foods or high-quality supplements, if you choose to take them, is a better health choice.
We all come into this life with a body, yet we're not given an operating manual. Where are those high-school courses that tell us how to maintain our health??? Most doctors aren't educated in preventative care either. It ultimately falls on you to educate yourself to maintain your own health. As people in our 50's who have spent decades of our lives in health care professions, we've seen how important it is to maintain one's health rather than fix problems later in life. We'd much rather be on grand adventures for the next 30 years than in a doctor's office!
To help you understand what you need to maintain a healthy vegan body we're going to share some of the latest research around plant-based nutrition. You'll see what vitamins and minerals some vegans miss out on and where to get them in your plant-based diet to help ensure your body has all the building blocks it needs for optimal energy levels, strength, and health.
We'll start by looking at a few vitamins. Click on each one if you want to jump directly to that section.
Being a smart vegan means paying attention to your diet to make sure you are getting all your nutrient needs met. If it's difficult for you to access a broad range of foods or you simply don't want to eat a varied plant-based diet, you may be vulnerable to nutrient deficiencies and want to explore vitamin supplementation. Of course, this is true of any type of diet- the standard American diet, flexitarian, pescatarian, vegetarian, or vegan.
To ensure that our intake of these required nutrients is met, we take a daily multivitamin with high levels of Vitamin B12 as well as a DHA/EPA algae-derived Omega 3 supplement, and a seasonal Vitamin D. Here are the specific ones we've researched and chosen:
Omega 3 Fatty Acids DHA and EPA
Master the Foundational Skills for Nutritious Plant-Based Cooking
Get on the waiting list and be the first to hear when this course launches. No obligation.

Vegan Sources of B12
Vitamin B12 is produced by bacteria and not plants. Most plant-based foods do not contain vitamin B12. Animals, and sometimes humans, get B12 when we eat bacteria from unwashed produce. (Go backyard gardens!) We also have gut bacteria that produce a small amount. It's important to maintain good digestive health and eat B12 rich foods whether you're vegan or omnivore. B12 is water-soluble so you will release any extra B12 through your urine. It's hard to get too much of it. Doses of up to 2,000 micrograms are considered safe, even though it's about 1,000 times what you need.
Why is vitamin B12 important?
- B12 is a co-factor in DNA, protein, and fatty acid synthesis, helping us maintain healthy levels of DHA and EPA.
- B12 is necessary to maintain normal-sized red blood cells and therefore helps prevent anemia.
- B12 is vital for healthy metabolism and nerves. Deficiency can cause numbness and tingling in your extremities.
- Normal levels of B12 provide energy levels that inspire us to continue the healthy activities that keep us feeling vital.
- B12 enhances our moods and helps our brains work better, including improved memory.
Where can I get vegan vitamin B12?
Nutritional yeast is one of our favorite plant-based sources of B12. We add it to all soups, stews, and dals, and we use it to add a cheesy flavor to many of our recipes like Pesto, and Mini Vegetable Souffles. Just 1 1/2 tsp of nutritional yeast meets the daily nutrient requirement for most adults. Get B12 fortified nutritional yeast here: Nutritional yeast.
Nori seaweed also contains vitamin B12. Our boys love Wasabi Seaweed snacks and Sea Salt Seaweed snacks. They eat them at least once per week. It takes specific gut bacteria to digest seaweed and research has shown that eating nori seaweed regularly will help you to develop and maintain the gut bacteria necessary to digest it.
You'll also get some when you eat B12 fortified foods, like cereals and vegan milk, and/or take a B12 supplement. Because we don't eat nutritional yeast and nori every day, we do take a multi-vitamin with high levels of it.
Nutritional tip: A health myth is that the superfood spirulina provides B12. While this is true, the B12 form in spirulina is a pseudo vitamin B12 that is not bioavailable to humans. Our bodies cannot use it. It does have many other health benefits and can be a great addition to your diet.
Nutritional tip: We only absorb small amounts of B12 at a time. Research suggests that taking smaller amounts of B12 more often is more beneficial.
How much vitamin B12 do you need?
Amounts are based on USDA, WHO, and/or European recommendations.
- Babies under 12 months need 0.4-0.5 micrograms (mcg) per day
- Children 1-3 years old need 0.9 mcg
- Children 4-8 years old need 1.2 mcg
- Kids 9-13 years old need 1.8 mcg
- Adults need 2.4 mcg
- Pregnant or lactating women need 2.6-2.8 mcg respectively
- If you're over 50 vitamin B12 is harder for you to absorb, so you may want to increase the amount you take in.
We get our B12 in this multi-vitamin: Genshai Multi-vitamin.
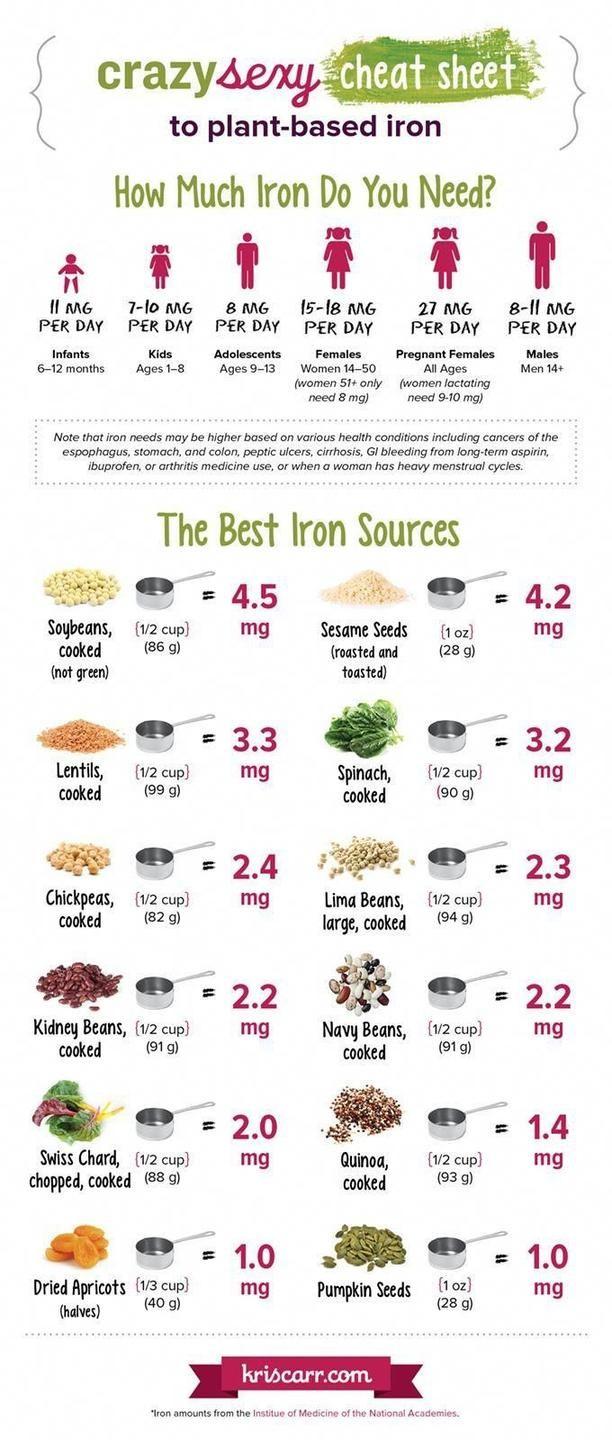
Getting Enough Vegan Iron
Iron is the mineral at the center of every blood cell that creates our oxygen delivery system. Anemia (iron deficiency) is a common nutrient deficiency in the USA. Heme iron comes from animals and non-heme iron comes from plants. Non-heme iron may not be as easy to absorb, so studies suggest getting more plant-based iron than the recommended daily allowances.
Why is Iron important?
If you're deficient in iron you may experience the following symptoms:
- extreme fatigue
- you lose a lot of hair each day and it doesn't grow back
- headaches and dizziness
- your tongue is sore
- cold hands and feet
- brittle nails
- impaired mental functioning
- delayed motor and mental development in infants
- low appetite in children
- pre-term and low birth weight babies
Looking on the positive side, adequate iron levels help you feel fabulous and have beautiful hair and nails!
Iron deficiency is common, especially in women because of our monthly blood loss through menstruation, regardless of dietary choices. Because B12 is also necessary for the absorption of iron, ensuring you ingest enough B12 will help you maintain adequate levels of iron. When you look at the nutritional analysis of many of the plant-based recipes on our blog, you'll see they contain heaps of iron and the Vitamin C, folate, and zinc needed to absorb it. Iron is an easy nutrient to source in a plant-based diet.
How much Iron do you need?
Iron needs vary. Amounts we post are based on USDA, WHO, and/or European recommendations.
Here are recommended daily iron intake suggestions:
- Kids ages 1-8 need 7-10 mg
- Kids ages 9-13 need 8 mg
- Women ages 14-50 need 15-18 mg
- Males over 14 need 8-11 mg
- Pregnant women need 27 mg
What foods are rich in Iron?
Soybeans, sesame seeds, spinach, and lentils are good plant-based sources of iron. If you look through our recipes you'll see that we easily exceed our iron requirements through the foods we eat.
Get your vegan iron in the following recipes:
- Sweet Sesame Snacks contain 20% (4 mg) of the US Recommended Daily Amount (RDA) of iron.
- Three Lentil Dal contains 23% of the US RDA.
Vegan Vitamin D
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble nutrient (meaning it's fat-based and doesn't dissolve in water. Vitamins A, E, and K are also fat-soluble). It's not a common vitamin in plant-based diets and is heavily fortified in our foods.
Why is Vitamin D important?
Vitamin D is a key player for strong bones, teeth, and muscles. It facilitates proper levels of Calcium and Phosphorus. It also builds our immune system, making us less prone to getting colds and flu. Vitamin D deficiency is linked to breast cancer, colon cancer, prostate cancer, heart disease, depression, and weight gain.
Vitamin awareness: Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin and if you take too much in supplement form your body can't get rid of the excess easily. Studies show that 10,000 IU over several months can cause kidney damage and that up to 2,000 IU per day is considered safe for maintaining proper vitamin D levels.
You can get a blood test to check your initial levels and monitor your blood levels if you take high doses of the fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K.
How much Vitamin D do you need?
The recommended daily intake for vitamin D is 600 IU (15 micrograms) for people ages 1-70. If you're over 70 years old, 800 IU (20 micrograms) is recommended. Amounts are based on USDA, WHO, and/or European recommendations.
Where do I source Vitamin D?
Vitamin D is found in a typical vegan diet through fortified foods, mushrooms, and sunlight on your skin. Yes, you can make Vitamin D! Studies suggest fifteen minutes of direct summer sun exposure to a large proportion of your skin (think shorts and a tank top or swimsuit) is enough for your daily dose of vitamin D. If this isn't possible for you year-round, look to fortified plant-based milks and cereals for some of your vitamin D and consider taking a supplement. Vitamin D is crucial for strong bones and a healthy immune system. You can order the one we seasonally take here: Vitamin D.
Nutrition tip: Like us, Mushrooms make vitamin D when exposed to sunlight. Scientific studies show that 100 gm of mushrooms that have been sliced and set in the sun for an hour can provide your daily Vitamin D requirement! The gills on the undersides make vitamin D faster than the tops.


Vegan Omega 3 Needs: DHA and EPA
Perhaps you've heard that Omega 3 essential fatty acids are important for your health. ALA (alpha-linolenic acid) is one of them and is considered essential because we can only get it from our food, we can't make it. Two other Omega 3 oils we need are DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) and EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid).
For vegans, it's easy to get healthy amounts of Omega 3s in your diet, but most of those will be ALA. It's not as easy to get enough DHA and EPA. Our bodies do convert ALA into the DHA and EPA we need, but not very efficiently. Because DHA and EPA are so important for our health, we do take a plant-based supplement: Omega 3 DHA and EPA.
Why do you need DHA and EPA?
EPA is critical for cardiovascular health and helpful for depression and menopause. It reduces pain and inflammation, the source of many chronic diseases.
DHA is important to prevent heart disease. It improves your memory and brain function and is especially important for mental development in children. It also supports eye and nerve health, showing positive results to prevent macular degeneration.
How much Omega 3 fatty acids do you need?
The following recommended daily allowances are for ALA only, and like all RDA represents the minimum needed to avoid deficiency symptoms. Amounts are based on USDA, WHO, and/or European recommendations.
- Kids 1-3 years old need 0.7 grams (gm)
- Kids 4-8 need 0.8 gm
- Kids 9-13 males need 1.2 gm, females need 1.0
- Males 14+ years need 1.6 gm and females need 1.1 gm
- Pregnant and lactating women need 1.4 and 1.3 gm respectively
Where do I source Omega 3 DHA and EPA?
What most people do not know is that there are three necessary types of Omega 3 essential fatty acids and ALA is the only one commonly available in plant-based foods. DHA and EPA are commonly found in seafood and also algae. You find it in seafood because fish eat the algae! We cut out the middle man, or middle fish, and take an algae-based EPA/DHA supplement: Omega 3 DHA/EPA.
You can increase your intake of ALA Omega 3 essential oils (remember we convert it to DHA and EPA) through the following foods:
- flaxseed oil
- chia seeds
- hemp seeds
- canola oil
- soybean oil
- edamame (whole soybeans often found in the frozen food section)
- navy beans
- avocados
- whole wheat bread
- oatmeal
Do you want the best for your family?
We bring families together around food.
Click HERE to explore the best way to meet my family's unique needs.
Meeting Your Plant-Based Protein Requirements
Many new vegans wonder where they will get their protein when they no longer eat meat or dairy products. After analyzing many recipes and meals it's clear that one can easily meet their protein needs with plants. In fact, many pro-athletes, extreme sports participants, and some of the strongest men in the world eat plant-based diets.
You know the key to meeting your protein needs is eating a smart vegan diet. With a little education and awareness, you'll be able to get plenty of protein without eating meat replacements, protein powders, or massive amounts of tofu.
Where can I find my protein?
Protein abounds in nuts, beans, lentils, and peas, soy products, and dark green vegetables. If you cook whole foods and eat across a variety of foods and cultures, you'll be amazed at how easy it is to get heaps of protein!
Here are some of the highest protein food sources for vegans:
Seitan: a wheat protein concentration with a meat-like texture. 25 grams of protein per 3.5 oz (100 grams).
Tofu: 17 grams of protein per 3.5 oz (10 grams)
Cooked edamame (fresh green soybean often found frozen in bags and a common side dish at Japanese restaurants): 17 grams of protein per 3.5 oz (100 grams).
Lentils, beans, and dried peas are collectively known as pulses. They average 9 grams of protein per 3.5 oz (100grams) of cooked
Most nuts average 6 grams of protein per ounce (one handful).
Vegetables also contain protein. You'll find 2.4-5 grams of protein per 3.5 oz (100 grams) in green peas, spinach, collard greens, artichokes, asparagus, Brussel sprouts, mushrooms, and broccoli.
How much protein do I need?
The amount of protein you need changes with your age and is affected by your activity level (athletes need more). Large nutritional studies have shown that if an average of 10% of your daily calories come from protein, you're getting enough. An average guideline is 0.38 grams of protein per pound of body weight for adults, or 0.83 grams per kilogram of bodyweight. The following are USDA recommendations.
- Babies require about 10 grams per day.
- School-age children require 19-34 grams per day.
- Teenage boys require up to 52 grams per day.
- Menstruating teenage girls require about 46 grams per day.
- Adult men require about 56 grams per day.
- Adult women require about 46 grams per day.
- Pregnant or breast-feeding women need approximately 71 grams per day.
Besides protein, you'll get loads of fiber, vitamins, minerals, and enzymes when you include raw foods in your diet too.
Living a thriving vegan lifestyle can be fun, adventurous, delicious, easy and nutritious. After eating a plant-based diet for 26+ years and with our backgrounds in Asian and Western medicine we're uniquely positioned to support your journey.
We hope this page has helped you understand how you can meet your body's nutritional needs with plant-based choices.
If you would like to learn more and become a part of our Vegan Family
- Cook with us in the Vegan Foodie Social Club
- Get on the waiting list for our course: Mastering the Foundations of Nutritious Plant-Based Cooking
- Schedule a complimentary call to explore how you can help your family thrive with a plant-based diet

Join Your Thriving Vegan Family Online Community
A private forum for vegan families and plant-based enthusiasts who are serious about maintaining a thriving, lifelong, vegan lifestyle.
Our mission is to inspire healthy, high-performance diets and lifestyles for excellence-driven people. Information and resources are for informational purposes only and are not intended to diagnose, treat, or cure any type of disease or condition.

